Understanding the various types of refrigerator condensers enhances our choice of appliances. A refrigerator condenser is crucial for cooling. It works by releasing heat from the refrigerant, which helps maintain the desired temperature inside the fridge.
There are several types of refrigerator condensers. Each functions uniquely, which can affect performance and efficiency. Some may prefer air-cooled condensers for their simplicity. Others might choose water-cooled for their efficiency. This variety can make decisions overwhelming.
Choosing the right type can lead to energy savings and a longer appliance life. However, it’s essential to consider installation and maintenance. Often, we overlook these aspects. Making a smart choice requires deeper understanding and reflection. Let's dive into the different types of refrigerator condensers you should know about.
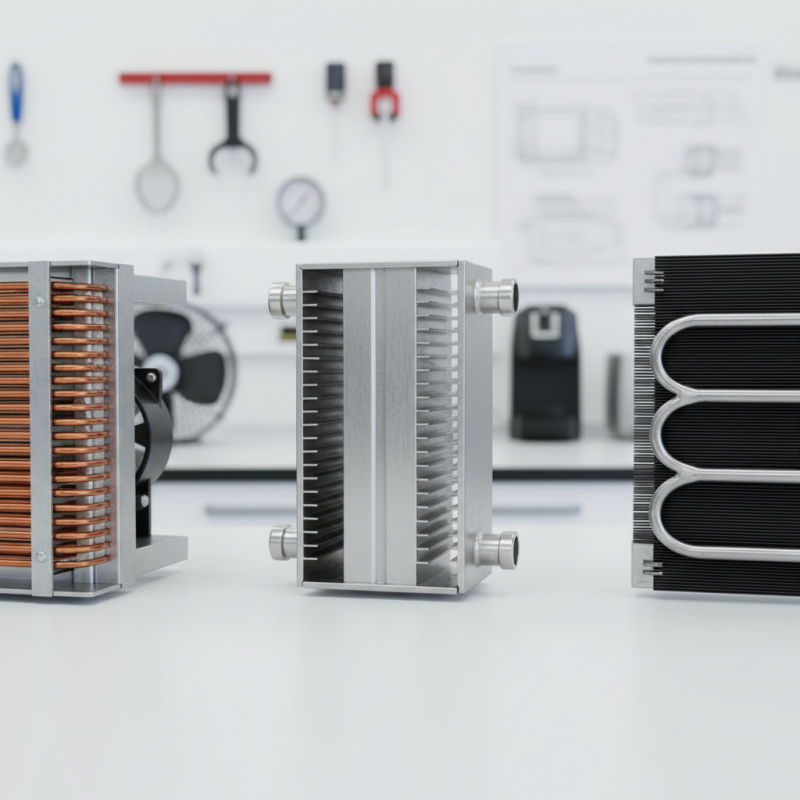

Refrigerators are essential kitchen appliances. Their efficiency often hinges on the type of condenser used. Understanding different condenser types can help you make informed choices.
There are generally three main types of condensers: air-cooled, water-cooled, and evaporative.
Air-cooled condensers are pivotal in various cooling systems. They work by dissipating heat from refrigerants into the ambient air. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, air-cooled units account for nearly 80% of all industrial systems. This high efficiency makes them increasingly popular in numerous applications, from refrigeration to air conditioning.
These condensers offer a range of benefits. They require less water than their water-cooled counterparts. A recent report from the American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers indicates that air-cooled systems can save up to 30% in operational costs where water is scarce. Moreover, their simple design allows for easier maintenance, reducing downtime.
However, in warmer climates, their efficiency can decline significantly. This can lead to higher operational costs during peak heat seasons.
In addition, noise can be a concern with air-cooled condensers. They often operate at higher sound levels than water-cooled systems. This might not suit all installations, particularly in residential areas. It raises questions about the balance between efficiency and acoustics, challenging engineers to innovate further. The industry must consider these trade-offs to optimize both performance and user satisfaction.
Water-cooled condensers are essential for many cooling applications. These systems use water to absorb heat from refrigerants. This method can be more efficient than air-cooled systems in certain settings. They work best in environments where water is readily available and the ambient temperature is controlled.
These condensers excel in commercial and industrial applications. Factories, data centers, and large buildings benefit greatly from their efficiency. However, their operation relies heavily on a consistent water supply. Inadequate water flow can lead to performance issues. It’s crucial to ensure proper maintenance and monitoring to prevent unwanted downtime.
Some challenges come with water-cooled condensers. They can suffer from scale buildup, which affects efficiency. Constant cleaning and chemical treatments may be necessary. Also, in areas with strict water usage regulations, their feasibility may be limited. These factors highlight the need for careful consideration before choosing this type of condenser.
This chart illustrates the efficiency of water-cooled condensers across different system sizes, highlighting their effectiveness in cooling applications. As the scale of the system increases, the efficiency tends to rise, showcasing the advantages of larger installations in thermal management.
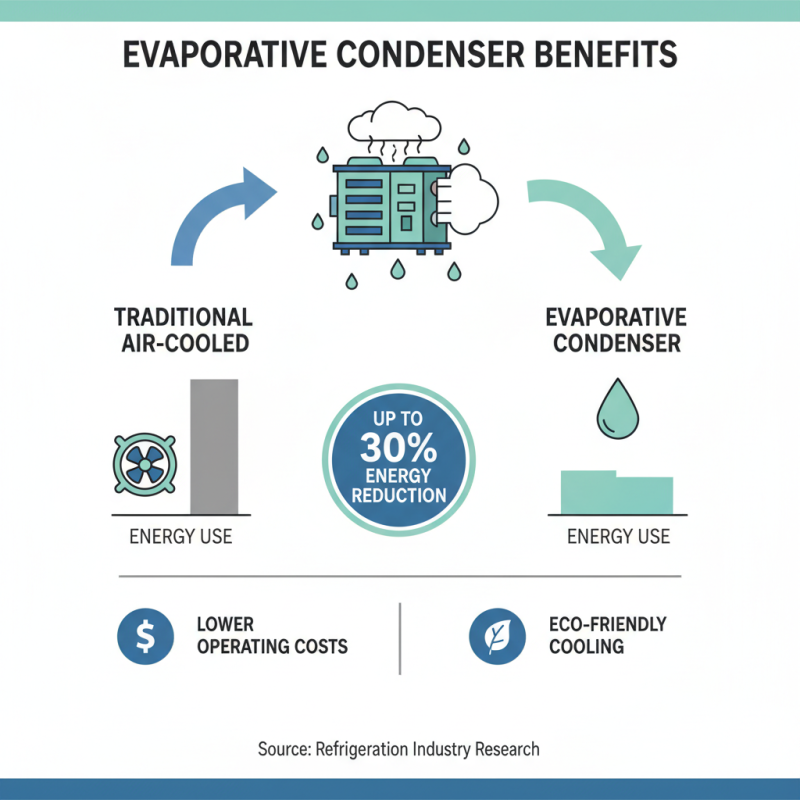
Evaporative condensers are gaining attention in the refrigeration industry for their efficiency. These systems utilize the cooling power of water evaporation to condense refrigerants. Research indicates that they can reduce energy usage by up to 30% compared to traditional air-cooled units. This significant reduction in energy consumption is a major draw for businesses looking to lower operating costs.
Features of evaporative condensers include a compact design and lower environmental impact. They require less energy to operate, making them more sustainable. Many systems are designed to operate effectively in varying climatic conditions. However, they do need regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance. Failure to maintain these systems can lead to reduced efficiency and potential breakdowns. The initial investment may seem high, yet the long-term savings can offset this.
Evaporative condensers can also be used in large-scale refrigeration applications, such as supermarkets and food storage facilities. In these settings, the ability to manage heat more effectively is crucial. Some reports suggest that operators can experience a 15% increase in cooling capacity. Still, it's essential to monitor water supply closely to prevent issues. Balancing cost-efficiency with reliability remains a challenge for many facilities using these units.
Hybrid condensers represent a significant evolution in refrigeration technology. These systems combine various cooling approaches. The idea is to leverage the strengths of each method. According to a report from the International Journal of Refrigeration, hybrid condensers can increase energy efficiency by up to 30%. This is a substantial improvement compared to traditional systems.
By integrating air and water cooling, hybrid condensers can adapt to different conditions. They often perform well in fluctuating environments. For example, during hot days, they may rely more on air cooling. When temperatures drop, water cooling becomes more efficient. This adaptability can lead to lower operational costs. However, the complexity of hybrid designs may create maintenance challenges.
Users must understand the balance between performance and upkeep. While hybrid systems offer benefits, they are not foolproof. The performance may vary based on installation quality. Moreover, not all environments are suitable for such condensers. In some cases, hybrid options may require more frequent checks. It's vital to analyze specific needs to avoid potential pitfalls.