Author:
-
Position:
General Manager of Foreign Trade Department, Taojun Refrigeration -
Professional Experience:
Engaged in international trade within the refrigeration industry since 2004.
Expert in brand strategy and omni-channel marketing, having led three multi-million yuan projects that boosted brand exposure by over 200%.
-
Core Competencies:
Proficient in data analysis and user growth strategies.
Skilled in SEO/SEM and social media management tools.
Experienced in cross-departmental collaboration and team leadership.
-
Philosophy:
"Data-driven decisions, creativity-powered branding." Committed to achieving business value and user experience excellence through refined operations. -
Vision:
Eager to collaborate with partners to explore emerging market opportunities and set industry benchmark cases.
Contact Us to Find More Products
Top 3 charging hose secrets for HVAC success

HVAC technicians rely on precise tools for optimal system performance. The Charging Hose plays a critical role in accurate diagnostics. Professionals use it to ensure exact refrigerant levels, which is essential for efficiency. Understanding proper techniques helps avoid common mistakes. This leads to more reliable HVAC system operation.
Key Takeaways
- Choose the right charging hose. Match its material and pressure rating to the job. This keeps you safe and helps the hose last longer.
- Connect and purge hoses carefully. Secure connections stop leaks. Purging removes bad air and water from the system.
- Use charging hoses for correct readings. This helps you find and fix HVAC problems. It makes sure the system works well.
- Clean and store your hoses properly. Check them often for damage. Replace old hoses to keep your work accurate and safe.
Secret 1: Understanding Charging Hose Types and Applications

Choosing the Right Charging Hose Material and Pressure Rating
Selecting the correct charging hose material and pressure rating is fundamental for HVAC technicians. The hose's construction directly impacts its safety and performance. A robust design ensures durability and reliability under demanding conditions. For instance, a charging hose with a distinctive three-layered design offers enhanced structural integrity. This construction often includes materials providing exceptional chemical, heat, and impact resistance. Technicians must consider the working and burst pressures to prevent failures.
| Material | Working Pressure (psi) | Burst Pressure (psi) |
|---|---|---|
| Nylon Core with Rubber Cover | 800 | 4000 |
| Kevlar with Nitrile Cover | 800 | 4000 |
| Kevlar (CL series) | 750 | 3000 |
These specifications ensure the hose withstands the high pressures encountered in HVAC systems. A wide temperature range, such as -40℃ to 95℃, further guarantees stable performance in extreme climates.
Decoding Charging Hose Color-Coding and Connections
Industry standards simplify the identification and connection of charging hoses through color-coding. This system helps technicians quickly distinguish between different lines.
- Standard 1/4" flare fittings are common.
- Hoses are color-coded yellow, blue, and red for easy recognition.
- They are compatible with various refrigerants including CFC, HFC, and HCFC (e.g., R-410A, R-404A, R-407C & R-134a).
End fittings must match the connected components, considering factors like O-ring style versus beadlock and specific thread types. SAE J2064 compliance ensures adherence to industry standards for construction, performance, and labeling.
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Connection Type | 1/4" SAE female flare with depressor and 45° fitting |
| Color Coding | Red, Blue, Yellow |
| Application | Charging, recovery, and evacuation |
This standardization streamlines operations and minimizes errors.
Specialized Charging Hoses for Vacuum and Control
Beyond standard charging, specialized hoses cater to specific HVAC tasks like vacuum and control. These hoses often feature enhanced flexibility and memory, allowing for easy bending and reducing the need for multiple joints. This design minimizes the risk of leaks. A smooth inner wall design also contributes to energy efficiency by reducing fluid resistance. Furthermore, the commitment to sanitary safety, with inner layer materials meeting national drinking water standards, ensures water quality over time. All materials are recyclable, aligning with environmental standards.
Secret 2: Mastering Charging Hose Connection and Purging
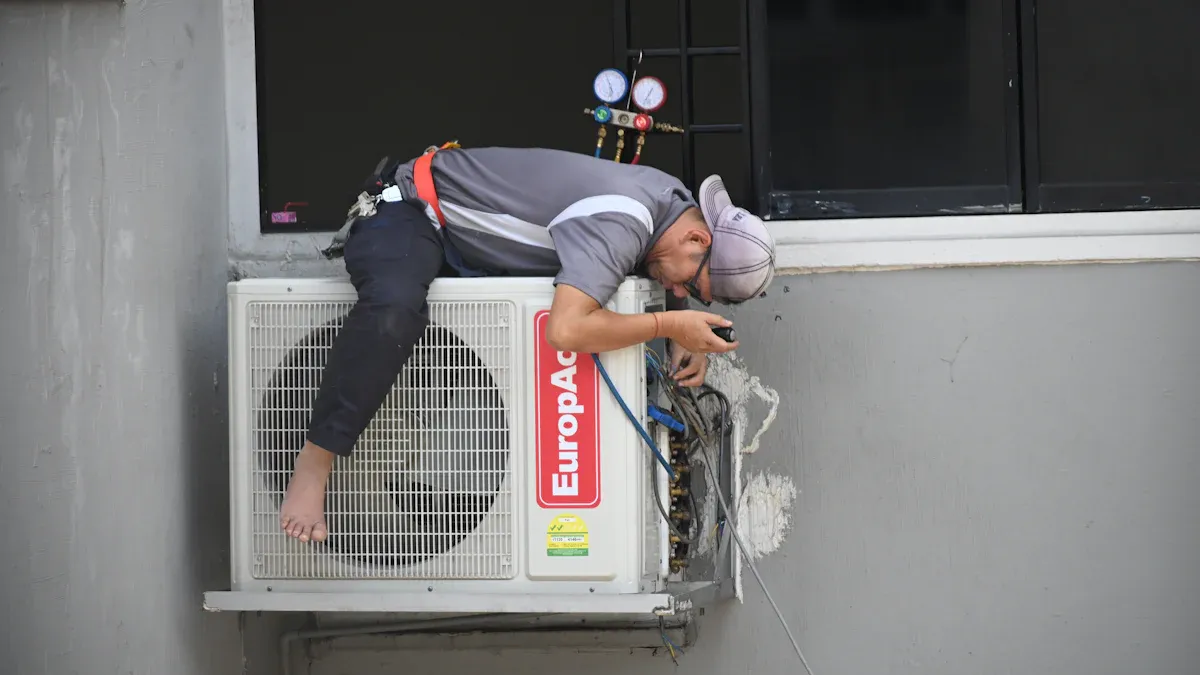

Secure Charging Hose Connections to Prevent Leaks
Properly securing charging hose connections is paramount for preventing refrigerant leaks and ensuring system efficiency. Technicians must always use a calibrated torque wrench. They follow manufacturer specifications for torque values. This practice prevents both over-tightening and under-tightening. Over-tightening can damage fittings, while under-tightening leads to leaks. Utilizing torque wrenches specifically calibrated for AC fittings is crucial. Incorrect torquing, whether excessive or insufficient, causes immediate leaks, damaged threads, or crushed components. This significantly reduces the system's lifespan.
The Importance of Purging Charging Hoses for System Integrity
Purging charging hoses is a critical step for maintaining HVAC system integrity. This process removes non-condensable gases, such as air and moisture, from the hoses before connecting them to the system. Air and moisture introduce contaminants that degrade refrigerant performance and can lead to system failure. Technicians perform purging by briefly opening the manifold valves to allow a small amount of refrigerant to flow through the hoses, expelling unwanted elements. This ensures only pure refrigerant enters the system, optimizing its operation and longevity.
Minimizing Refrigerant Loss During Charging Hose Disconnection
Minimizing refrigerant loss during charging hose disconnection is an essential practice for environmental protection and cost efficiency. Technicians employ specific tools and techniques to achieve this. Charging hoses equipped with ball valves allow precise control over refrigerant flow. These valves help trap refrigerant within the hoses, significantly reducing loss during disconnection. Shorter hoses also minimize the volume of refrigerant contained within the hose, further reducing potential loss. Core depressors must be properly exposed, and their seals must be in good condition. This ensures efficient refrigerant flow and prevents leaks during connection and disconnection. Specific tools, such as those with backseat control valves, are also available to manage refrigerant flow effectively.
Secret 3: Accurate Charging and Diagnostics with Charging Hoses
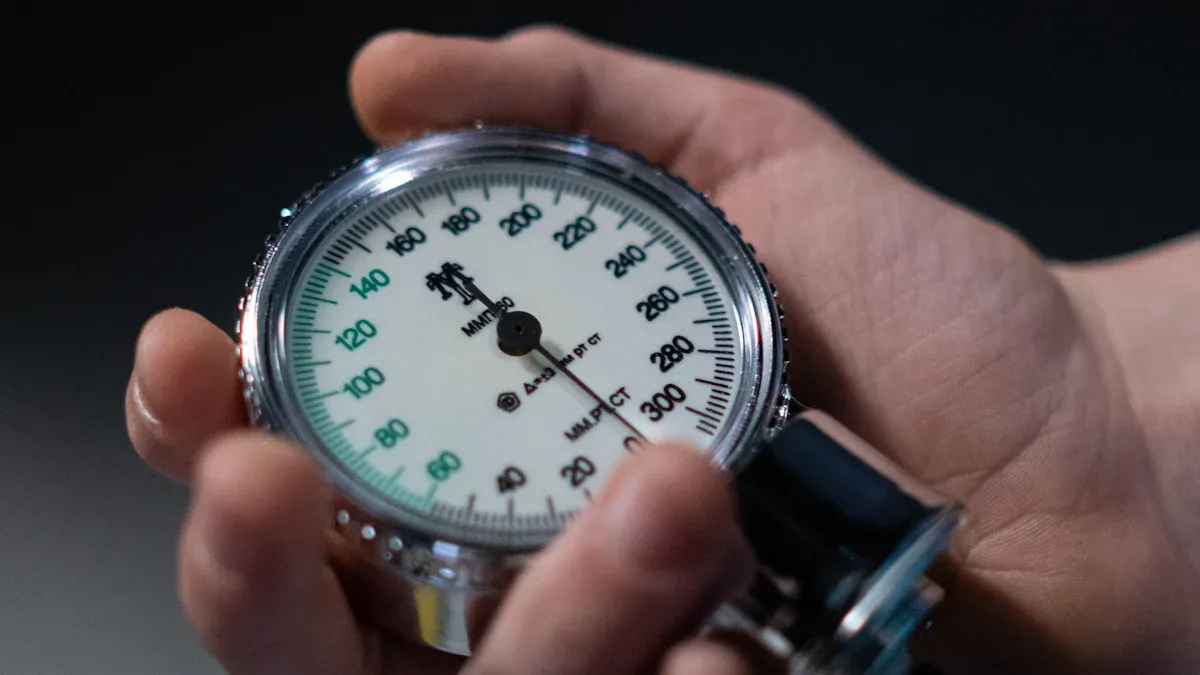

Connecting Charging Hoses for Precise Pressure Readings
Accurate pressure readings are fundamental for effective HVAC diagnostics. Technicians must connect charging hoses correctly to obtain reliable data. First, they turn off the HVAC system's power. Then, they open the access valves on the Manifold Gauge Set. Technicians connect the blue hose to the low-pressure (suction) side and the red hose to the high-pressure (discharge) side. The yellow hose typically serves for refrigerant charge or vacuum. For precise readings, theyconnect the red hose and red gauge to the high-pressure port. Similarly, they connect the blue hose and blue gauge to the low-pressure port. After connecting, technicians start the refrigeration system and allow it to stabilize for a few minutes. They then read the pressures on the gauges, ensuring compatibility with the refrigerant and correct units.
Safe and Accurate Refrigerant Charging Procedures
Safe and accurate refrigerant charging requires adherence to industry standards and best practices. Technicians must hold EPA 608 Certification, which demonstrates knowledge of the Clean Air Act and proper procedures. This certification includes types for small appliances, high-pressure systems, and low-pressure chillers. Essential safety equipment includes safety glasses, chemical-resistant gloves, and long clothing. Technicians also use electronic refrigerant detectors and digital manifold gauges. Before starting, they assess the work environment for hazards and ensure adequate ventilation. They always follow manufacturer specifications for refrigerant type and quantity. Technicians charge liquid refrigerant into the high-pressure side when the system is off. They charge vapor into the low-pressure side during operation. Never charge liquid into a running compressor's suction line. Different refrigerants, like R-32 or R-134a, have unique handling characteristics and safety considerations.
Troubleshooting HVAC Issues Using Charging Hose Insights
Charging hose insights are invaluable for troubleshooting HVAC issues. Technicians use the pressure readings obtained through the charging hose connections to diagnose system problems. Abnormally high or low pressures on either the suction or discharge side indicate specific malfunctions. For example, consistently low suction pressure might suggest a refrigerant undercharge or a restricted flow. Conversely, high discharge pressure could point to an overcharge or a condenser issue. By comparing these readings against manufacturer specifications and refrigerant pressure-temperature charts, technicians can pinpoint the root cause of performance issues. This diagnostic approach allows for targeted repairs, improving system efficiency and reliability.
Secret 4: Maintaining Your Charging Hoses for Longevity and Accuracy
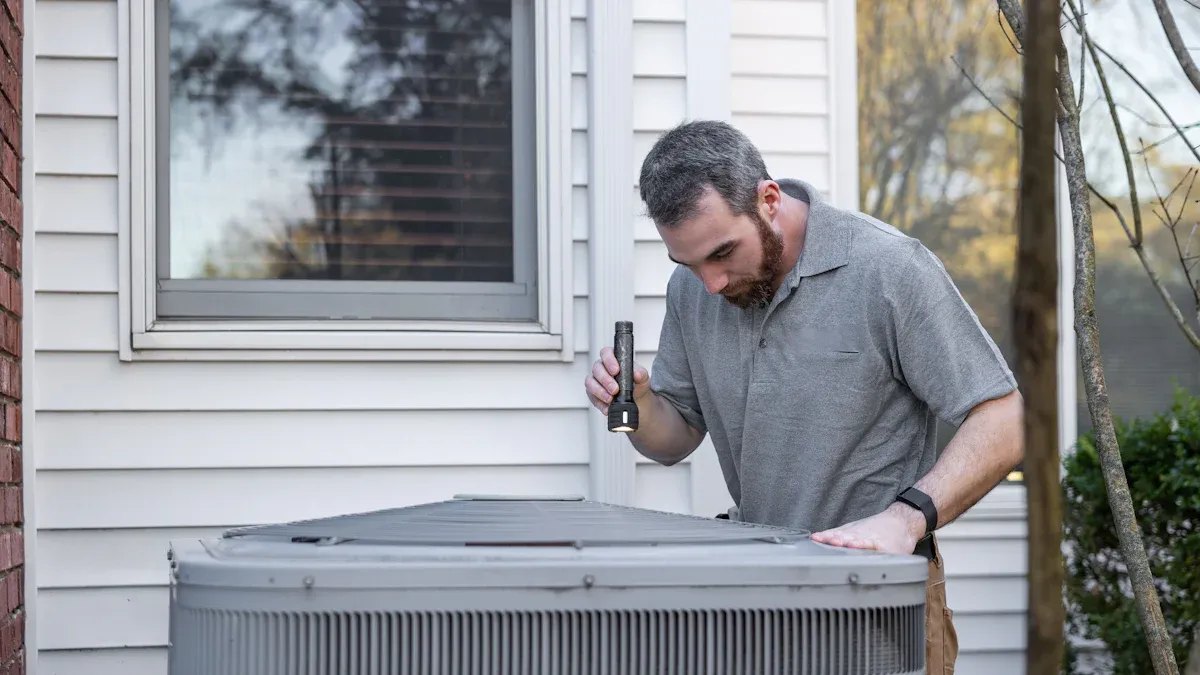

Proper Cleaning and Storage of Charging Hoses
Technicians must prioritize proper cleaning and storage for charging hoses to ensure their longevity and maintain accuracy. After each use, they should wipe down hoses to remove any refrigerant oil or debris. This prevents contamination and preserves the hose material. Storing hoses in a cool, dry place, away from direct sunlight and extreme temperatures, helps prevent material degradation. Coiling hoses loosely, rather than kinking them tightly, also extends their life. Using protective caps on fittings prevents dirt and moisture from entering, which safeguards internal components.
Inspecting Charging Hoses for Wear and Damage
Regular inspection of charging hoses is crucial for identifying potential issues before they lead to system failures or refrigerant leaks. Technicians should look for visible damage such as cracks, bulges, or fraying on the hose assemblies. They also check for corrosion or looseness in hose connectors. Other critical indicators include oily residue around connections or frost buildup on hoses and fittings. These signs often point to leaks or material fatigue. Ignoring these warnings can compromise system integrity and technician safety.
When to Replace Your Charging Hoses
Knowing when to replace charging hoses is as important as proper maintenance. Technicians should consider replacement if they observe any of the wear and damage indicators during inspection. Drops in cooling efficiency or unusual noises during AC operation can also signal hose issues. While automotive AC hoses typically have a lifespan of 5-7 years, this serves as a general timeframe. The actual need for replacement depends on usage frequency, handling, and environmental exposure. Proactive replacement prevents unexpected failures and ensures consistent, accurate HVAC service.
Technicians implement these charging hose secrets for enhanced HVAC troubleshooting. They achieve more efficient and reliable HVAC system performance. Mastering these expert charging hose techniques elevates their HVAC repair capabilities.
By applying these principles, professionals ensure precise refrigerant levels and prevent costly system failures.
This comprehensive approach leads to optimal system function and increased client satisfaction. It also extends the lifespan of HVAC systems.
FAQ

What is the main function of a charging hose in HVAC?
A charging hose connects HVAC systems to manifold gauges or refrigerant tanks. It allows technicians to accurately measure system pressures. It also facilitates the safe transfer of refrigerant for charging or recovery. This ensures optimal system performance.
Why do technicians purge charging hoses?
Technicians purge charging hoses to remove air and moisture. These contaminants degrade refrigerant performance. Purging prevents them from entering the HVAC system. This maintains system integrity and extends equipment lifespan.
How often should technicians replace charging hoses?
Technicians should replace charging hoses based on wear and damage. Look for cracks, bulges, or fraying. While automotive hoses last 5-7 years, usage frequency dictates replacement. Proactive replacement prevents failures and ensures accurate service.
Can technicians use one charging hose for all refrigerants?
No, technicians cannot use one charging hose for all refrigerants. Different refrigerants require specific hose types and pressure ratings. Hoses are often color-coded for compatibility. Using the correct hose prevents cross-contamination and ensures safety.